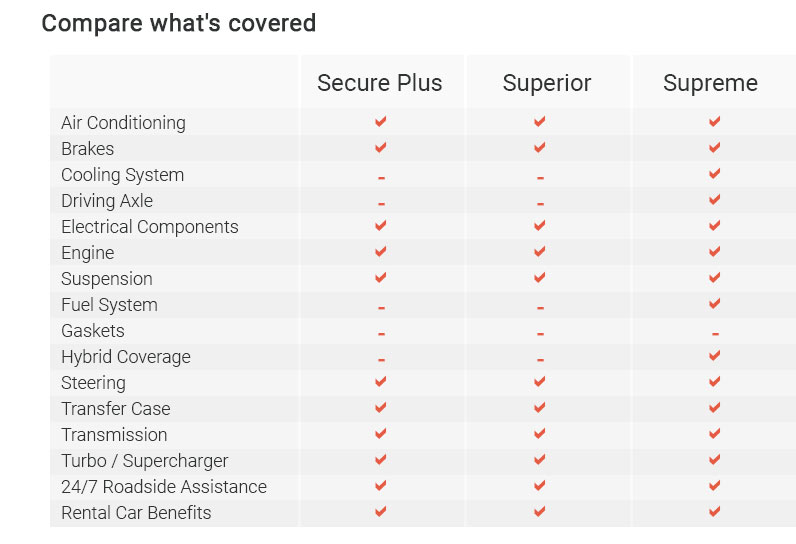
toyota warranty essentials for new and used ownersClear, practical coverage can save hours and money. This guide shows what's protected, what isn't, and the fastest ways to use your benefits. What the core coverage usually meansToyota splits protection into several buckets. They work together but cover different failures. Think layers rather than one blanket. - Basic (bumper-to-bumper): Defects in materials or workmanship on most parts; typically shorter in duration but broad in scope.
- Powertrain: Engine, transmission/transaxle, and related internal parts; usually longer, but narrower.
- Corrosion perforation: Rust-through of sheet metal; cosmetic surface rust isn't the same thing.
- Hybrid/EV systems: High-voltage battery, inverter, motor, and related components; terms vary by model year and region, with newer hybrids often enjoying notably extended battery coverage.
- Emissions: Certain components have federally mandated coverage; lengths differ by part and state rules.
- Accessories: Toyota Genuine Accessories installed at purchase are commonly covered; dealer-installed later may have different terms.
- Roadside assistance: Time-limited help for jump-starts, lockouts, towing; useful but separate from repair coverage.
- Maintenance plans: Items like oil changes are service programs, not warranty; helpful, but they don't replace defect coverage.
What's not covered (and why that matters)- Wear items: Brake pads, wiper blades, tires, and clutches wear out by design.
- Damage: Road hazards, collisions, floods, and environmental fallout are insurance topics, not warranty items.
- Neglect or misuse: Skipped maintenance, racing, overloading, or wrong fluids can void related claims.
- Aftermarket issues: A non-Toyota mod only affects warranty if it causes the failure, but the burden of proof matters.
- Alignment and trims: Often excluded unless a documented defect is the root cause.
- Tires: Typically handled by the tire manufacturer's warranty.
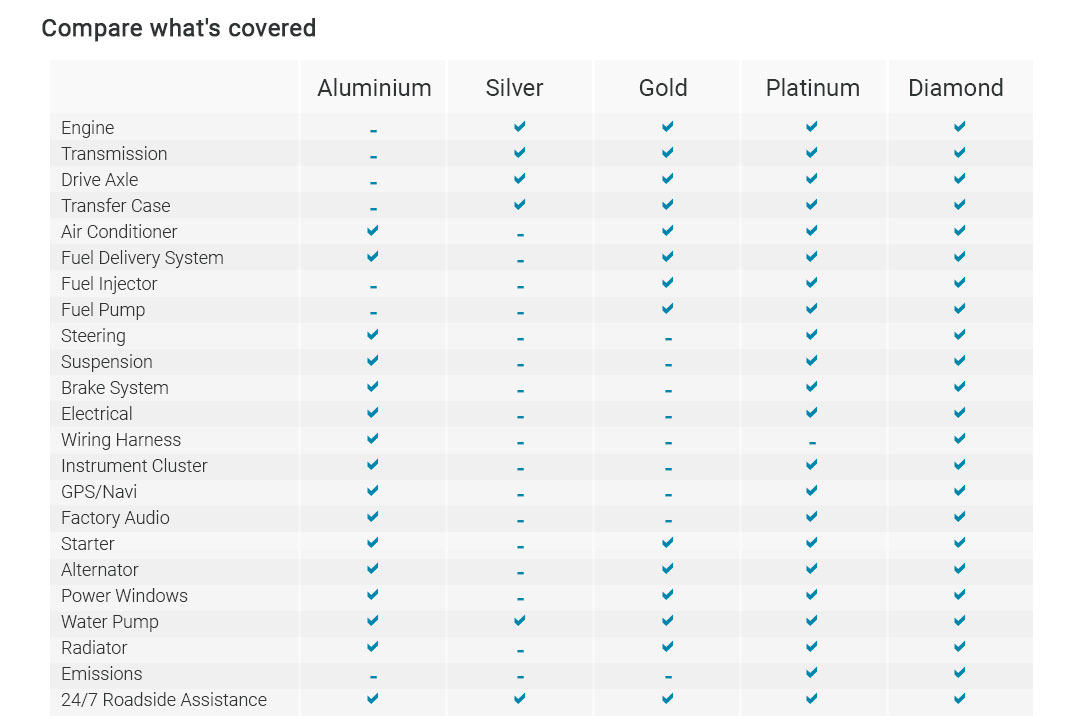
Quick comparison: warranty vs extended planA factory warranty covers defects for a defined time/mileage. An extended service plan (Toyota-backed or third-party) is a contract to pay for certain repairs after, or beyond, the factory term. One protects against build defects early; the other manages future risk. - Toyota-backed plans: Generally better part fitment, dealer network access, and clearer claim handling.
- Third-party contracts: Read for exclusions, deductibles, and pay-upfront rules; shop reputation matters more than brochure promises.
New, Certified Used, and private-party differences- New: Full new-vehicle coverage starts at the in-service date.
- Certified Pre-Owned: Adds an extra limited warranty and extended powertrain coverage, plus inspection benefits.
- Private-party: Remaining factory coverage usually follows the car; verify start date and mileage.
Action steps to check your coverage- Find the in-service date: Use your VIN in Toyota's owner portal or ask a dealer service advisor.
- Read the Warranty & Maintenance Guide: Scan the coverage charts and the exclusions page.
- Document symptoms: Note noise, frequency, warning lights, and conditions (cold start, uphill, rain).
- Book a diagnosis: Approve inspection first; authorize repair after coverage is confirmed.
- Keep records: Save receipts, oil change logs, and any photos or videos of the issue.
- Escalate if needed: Ask for the service manager or Toyota regional case if a claim seems misclassified.
A small real-world momentFriday evening, steady rain, your Corolla's screen goes black and won't reboot. You pull into a dealer Saturday morning; the advisor checks the VIN, confirms it's within the basic coverage window, and replaces the unit after verifying a known bulletin. You pick it up that afternoon - no charge, and your maintenance receipts made the conversation quick. Claim tips that save time- Arrive prepared: Bring registration, ID, and any prior repair orders.
- Ask about TSBs: A Technical Service Bulletin may streamline diagnosis.
- Be precise: "Rattle at 1,800 - 2,000 rpm on decel" beats "weird noise."
- Close to expiry? Request goodwill review if you're just outside time or mileage.
- Get details: Ask for replaced part numbers and the warranty labor op code for your records.
Hybrid and EV specifics- Battery coverage: Newer models often have longer high-voltage battery terms; confirm by model year and state.
- Covered components: Inverter/converter, drive motor, and HV ECU are typically included under hybrid system coverage.
- Maintenance matters: Cooling loops and software updates help longevity; keep intervals current.
- Capacity concerns: Some regions specify capacity criteria; testing procedures must be followed by the dealer.
Think of hybrid coverage another way: it's not only about the battery, but the ecosystem that powers and manages it. Before you buy (or before a long trip)- Verify status: Ask for a printout of warranty start date, remaining months/miles, and any open campaigns.
- Check history: Service records show care; consistency helps claim confidence.
- Recall note: Safety recalls are separate - free regardless of warranty time.
Keep receipts. In other words, proof of routine care supports coverage and shortens debates. A warranty isn't a promise of zero expense; it's a structured safety net. Framed differently, you're shifting defined risks to Toyota for a defined period - use that advantage with good documentation and timely action. 
|
|